-
1 control
[kən'trəul] 1. noun1) (the right of directing or of giving orders; power or authority: She has control over all the decisions in that department; She has no control over that dog.) pouvoir; autorité2) (the act of holding back or restraining: control of prices; I know you're angry but you must not lose control (of yourself).) contrôle, maîtrise de soi3) ((often in plural) a lever, button etc which operates (a machine etc): The clutch and accelerator are foot controls in a car.) commande(s)4) (a point or place at which an inspection takes place: passport control.) contrôle2. verb1) (to direct or guide; to have power or authority over: The captain controls the whole ship; Control your dog!) être maître de2) (to hold back; to restrain (oneself or one's emotions etc): Control yourself!) (se) maîtriser3) (to keep to a fixed standard: The government is controlling prices.) contrôler•- control-tower - in control of - in control - out of control - under control -
2 программируемый логический контроллер
программируемый логический контроллер
ПЛК
-
[Интент]
контроллер
Управляющее устройство, осуществляющее автоматическое управление посредством программной реализации алгоритмов управления.
[Сборник рекомендуемых терминов. Выпуск 107. Теория управления.
Академия наук СССР. Комитет научно-технической терминологии. 1984 г.]EN
storage-programmable logic controller
computer-aided control equipment or system whose logic sequence can be varied via a directly or remote-control connected programming device, for example a control panel, a host computer or a portable terminal
[IEV ref 351-32-34]FR
automate programmable à mémoire
См. также:
équipement ou système de commande assisté par ordinateur dont la séquence logique peut être modifiée directement ou par l'intermédiaire d'un dispositif de programmation relié à une télécommande, par exemple un panneau de commande, un ordinateur hôte ou un terminal de données portatif
[IEV ref 351-32-34]
- архитектура контроллера;
- производительность контроллера;
- время реакции контроллера;
КЛАССИФИКАЦИЯ
Основным показателем ПЛК является количество каналов ввода-вывода. По этому признаку ПЛК делятся на следующие группы:- нано- ПЛК (менее 16 каналов);
- микро-ПЛК (более 16, до 100 каналов);
- средние (более 100, до 500 каналов);
- большие (более 500 каналов).
- моноблочными - в которых устройство ввода-вывода не может быть удалено из контроллера или заменено на другое. Конструктивно контроллер представляет собой единое целое с устройствами ввода-вывода (например, одноплатный контроллер). Моноблочный контроллер может иметь, например, 16 каналов дискретного ввода и 8 каналов релейного вывода;
- модульные - состоящие из общей корзины (шасси), в которой располагаются модуль центрального процессора и сменные модули ввода-вывода. Состав модулей выбирается пользователем в зависимости от решаемой задачи. Типовое количество слотов для сменных модулей - от 8 до 32;
- распределенные (с удаленными модулями ввода-вывода) - в которых модули ввода-вывода выполнены в отдельных корпусах, соединяются с модулем контроллера по сети (обычно на основе интерфейса RS-485) и могут быть расположены на расстоянии до 1,2 км от процессорного модуля.
Многие контроллеры имеют набор сменных процессорных плат разной производительности. Это позволяет расширить круг потенциальных пользователей системы без изменения ее конструктива.
По конструктивному исполнению и способу крепления контроллеры делятся на:- панельные (для монтажа на панель или дверцу шкафа);
- для монтажа на DIN-рейку внутри шкафа;
- для крепления на стене;
- стоечные - для монтажа в стойке;
- бескорпусные (обычно одноплатные) для применения в специализированных конструктивах производителей оборудования (OEM - "Original Equipment Manufact urer").
По области применения контроллеры делятся на следующие типы:- универсальные общепромышленные;
- для управления роботами;
- для управления позиционированием и перемещением;
- коммуникационные;
- ПИД-контроллеры;
- специализированные.
По способу программирования контроллеры бывают:- программируемые с лицевой панели контроллера;
- программируемые переносным программатором;
- программируемые с помощью дисплея, мыши и клавиатуры;
- программируемые с помощью персонального компьютера.
Контроллеры могут программироваться на следующих языках:- на классических алгоритмических языках (C, С#, Visual Basic);
- на языках МЭК 61131-3.
Контроллеры могут содержать в своем составе модули ввода-вывода или не содержать их. Примерами контроллеров без модулей ввода-вывода являются коммуникационные контроллеры, которые выполняют функцию межсетевого шлюза, или контроллеры, получающие данные от контроллеров нижнего уровня иерархии АСУ ТП. Контроллеры для систем автоматизации
Слово "контроллер" произошло от английского "control" (управление), а не от русского "контроль" (учет, проверка). Контроллером в системах автоматизации называют устройство, выполняющее управление физическими процессами по записанному в него алгоритму, с использованием информации, получаемой от датчиков и выводимой в исполнительные устройства.
Первые контроллеры появились на рубеже 60-х и 70-х годов в автомобильной промышленности, где использовались для автоматизации сборочных линий. В то время компьютеры стоили чрезвычайно дорого, поэтому контроллеры строились на жесткой логике (программировались аппаратно), что было гораздо дешевле. Однако перенастройка с одной технологической линии на другую требовала фактически изготовления нового контроллера. Поэтому появились контроллеры, алгоритм работы которых мог быть изменен несколько проще - с помощью схемы соединений реле. Такие контроллеры получили название программируемых логических контроллеров (ПЛК), и этот термин сохранился до настоящего времени. Везде ниже термины "контроллер" и "ПЛК" мы будем употреблять как синонимы.
Немного позже появились ПЛК, которые можно было программировать на машинно-ориентированном языке, что было проще конструктивно, но требовало участия специально обученного программиста для внесения даже незначительных изменений в алгоритм управления. С этого момента началась борьба за упрощение процесса программирования ПЛК, которая привела сначала к созданию языков высокого уровня, затем - специализированных языков визуального программирования, похожих на язык релейной логики. В настоящее время этот процесс завершился созданием международного стандарта IEC (МЭК) 1131-3, который позже был переименован в МЭК 61131-3. Стандарт МЭК 61131-3 поддерживает пять языков технологического программирования, что исключает необходимость привлечения профессиональных программистов при построении систем с контроллерами, оставляя для них решение нестандартных задач.
В связи с тем, что способ программирования является наиболее существенным классифицирующим признаком контроллера, понятие "ПЛК" все реже используется для обозначения управляющих контроллеров, которые не поддерживают технологические языки программирования. Жесткие ограничения на стоимость и огромное разнообразие целей автоматизации привели к невозможности создания универсального ПЛК, как это случилось с офисными компьютерами. Область автоматизации выдвигает множество задач, в соответствии с которыми развивается и рынок, содержащий сотни непохожих друг на друга контроллеров, различающихся десятками параметров.
Выбор оптимального для конкретной задачи контроллера основывается обычно на соответствии функциональных характеристик контроллера решаемой задаче при условии минимальной его стоимости. Учитываются также другие важные характеристики (температурный диапазон, надежность, бренд изготовителя, наличие разрешений Ростехнадзора, сертификатов и т. п.).
Несмотря на огромное разнообразие контроллеров, в их развитии заметны следующие общие тенденции:- уменьшение габаритов;
- расширение функциональных возможностей;
- увеличение количества поддерживаемых интерфейсов и сетей;
- использование идеологии "открытых систем";
- использование языков программирования стандарта МЭК 61131-3;
- снижение цены.
[ http://bookasutp.ru/Chapter6_1.aspx]
Программируемый логический контроллер (ПЛК, PLC) – микропроцессорное устройство, предназначенное для управления технологическим процессом и другими сложными технологическими объектами.
Принцип работы контроллера состоит в выполнение следующего цикла операций:
1. Сбор сигналов с датчиков;
2. Обработка сигналов согласно прикладному алгоритму управления;
3. Выдача управляющих воздействий на исполнительные устройства.
В нормальном режиме работы контроллер непрерывно выполняет этот цикл с частотой от 50 раз в секунду. Время, затрачиваемое контроллером на выполнение полного цикла, часто называют временем (или периодом) сканирования; в большинстве современных ПЛК сканирование может настраиваться пользователем в диапазоне от 20 до 30000 миллисекунд. Для быстрых технологических процессов, где критична скорость реакции системы и требуется оперативное регулирование, время сканирования может составлять 20 мс, однако для большинства непрерывных процессов период 100 мс считается вполне приемлемым.
Аппаратно контроллеры имеют модульную архитектуру и могут состоять из следующих компонентов:
1. Базовая панель ( Baseplate). Она служит для размещения на ней других модулей системы, устанавливаемых в специально отведенные позиции (слоты). Внутри базовой панели проходят две шины: одна - для подачи питания на электронные модули, другая – для пересылки данных и информационного обмена между модулями.
2. Модуль центрального вычислительного устройства ( СPU). Это мозг системы. Собственно в нем и происходит математическая обработка данных. Для связи с другими устройствами CPU часто оснащается сетевым интерфейсом, поддерживающим тот или иной коммуникационный стандарт.
3. Дополнительные коммуникационные модули. Необходимы для добавления сетевых интерфейсов, неподдерживаемых напрямую самим CPU. Коммуникационные модули существенно расширяют возможности ПЛК по сетевому взаимодействию. C их помощью к контроллеру подключают узлы распределенного ввода/вывода, интеллектуальные полевые приборы и станции операторского уровня.
4. Блок питания. Нужен для запитки системы от 220 V. Однако многие ПЛК не имеют стандартного блока питания и запитываются от внешнего.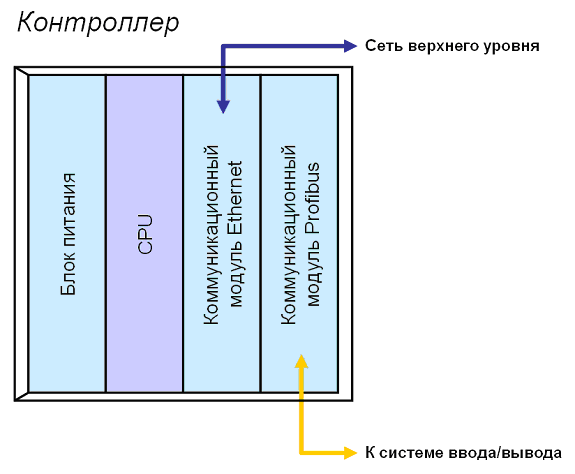 Рис.1. Контроллер РСУ с коммуникациями Profibus и Ethernet.
Рис.1. Контроллер РСУ с коммуникациями Profibus и Ethernet.
Иногда на базовую панель, помимо указанных выше, допускается устанавливать модули ввода/вывода полевых сигналов, которые образуют так называемый локальный ввод/вывод. Однако для большинства РСУ (DCS) характерно использование именно распределенного (удаленного) ввода/вывода.
Отличительной особенностью контроллеров, применяемых в DCS, является возможность их резервирования. Резервирование нужно для повышения отказоустойчивости системы и заключается, как правило, в дублировании аппаратных модулей системы.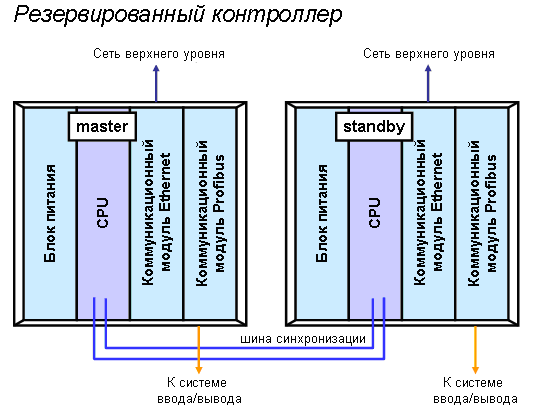 Рис. 2. Резервированный контроллер с коммуникациями Profibus и Ethernet.
Рис. 2. Резервированный контроллер с коммуникациями Profibus и Ethernet.
Резервируемые модули работают параллельно и выполняют одни и те же функции. При этом один модуль находится в активном состоянии, а другой, являясь резервом, – в режиме “standby”. В случае отказа активного модуля, система автоматически переключается на резерв (это называется “горячий резерв”).
Обратите внимание, контроллеры связаны шиной синхронизации, по которой они мониторят состояние друг друга. Это решение позволяет разнести резервированные модули на значительное расстояние друг от друга (например, расположить их в разных шкафах или даже аппаратных).
Допустим, в данный момент активен левый контроллер, правый – находится в резерве. При этом, даже находясь в резерве, правый контроллер располагает всеми процессными данными и выполняет те же самые математические операции, что и левый. Контроллеры синхронизированы. Предположим, случается отказ левого контроллера, а именно модуля CPU. Управление автоматически передается резервному контроллеру, и теперь он становится главным. Здесь очень большое значение имеют время, которое система тратит на переключение на резерв (обычно меньше 0.5 с) и отсутствие возмущений (удара). Теперь система работает на резерве. Как только инженер заменит отказавший модуль CPU на исправный, система автоматически передаст ему управление и возвратится в исходное состояние.
На рис. 3 изображен резервированный контроллер S7-400H производства Siemens. Данный контроллер входит в состав РСУ Simatic PCS7.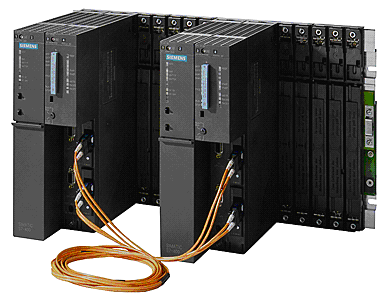 Рис. 3. Резервированный контроллер S7-400H. Несколько другое техническое решение показано на примере резервированного контроллера FCP270 производства Foxboro (рис. 4). Данный контроллер входит в состав системы управления Foxboro IA Series.
Рис. 3. Резервированный контроллер S7-400H. Несколько другое техническое решение показано на примере резервированного контроллера FCP270 производства Foxboro (рис. 4). Данный контроллер входит в состав системы управления Foxboro IA Series.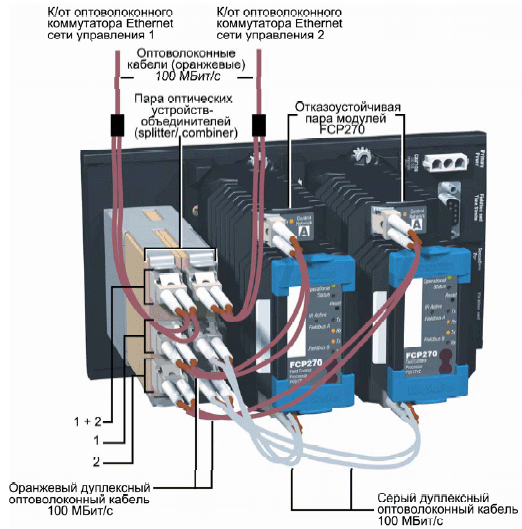 Рис. 4. Резервированный контроллер FCP270.
Рис. 4. Резервированный контроллер FCP270.
На базовой панели инсталлировано два процессорных модуля, работающих как резервированная пара, и коммуникационный модуль для сопряжения с оптическими сетями стандарта Ethernet. Взаимодействие между модулями происходит по внутренней шине (тоже резервированной), спрятанной непосредственно в базовую панель (ее не видно на рисунке).
На рисунке ниже показан контроллер AC800M производства ABB (часть РСУ Extended Automation System 800xA).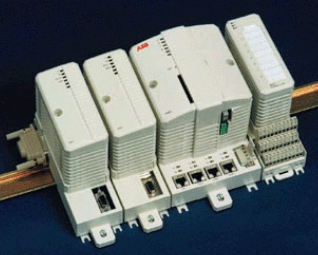 Рис. 5. Контроллер AC800M.
Рис. 5. Контроллер AC800M.
Это не резервированный вариант. Контроллер состоит из двух коммуникационных модулей, одного СPU и одного локального модуля ввода/вывода. Кроме этого, к контроллеру можно подключить до 64 внешних модулей ввода/вывода.
При построении РСУ важно выбрать контроллер, удовлетворяющий всем техническим условиям и требованиям конкретного производства. Подбирая оптимальную конфигурацию, инженеры оперируют определенными техническими характеристиками промышленных контроллеров. Наиболее значимые перечислены ниже:
1. Возможность полного резервирования. Для задач, где отказоустойчивость критична (химия, нефтехимия, металлургия и т.д.), применение резервированных конфигураций вполне оправдано, тогда как для других менее ответственных производств резервирование зачастую оказывается избыточным решением.
2. Количество и тип поддерживаемых коммуникационных интерфейсов. Это определяет гибкость и масштабируемость системы управления в целом. Современные контроллеры способны поддерживать до 10 стандартов передачи данных одновременно, что во многом определяет их универсальность.
3. Быстродействие. Измеряется, как правило, в количестве выполняемых в секунду элементарных операций (до 200 млн.). Иногда быстродействие измеряется количеством обрабатываемых за секунду функциональных блоков (что такое функциональный блок – будет рассказано в следующей статье). Быстродействие зависит от типа центрального процессора (популярные производители - Intel, AMD, Motorola, Texas Instruments и т.д.)
4. Объем оперативной памяти. Во время работы контроллера в его оперативную память загружены запрограммированные пользователем алгоритмы автоматизированного управления, операционная система, библиотечные модули и т.д. Очевидно, чем больше оперативной памяти, тем сложнее и объемнее алгоритмы контроллер может выполнять, тем больше простора для творчества у программиста. Варьируется от 256 килобайт до 32 мегабайт.
5. Надежность. Наработка на отказ до 10-12 лет.
6. Наличие специализированных средств разработки и поддержка различных языков программирования. Очевидно, что существование специализированный среды разработки прикладных программ – это стандарт для современного контроллера АСУ ТП. Для удобства программиста реализуется поддержка сразу нескольких языков как визуального, так и текстового (процедурного) программирования (FBD, SFC, IL, LAD, ST; об этом в следующей статье).
7. Возможность изменения алгоритмов управления на “лету” (online changes), т.е. без остановки работы контроллера. Для большинства контроллеров, применяемых в РСУ, поддержка online changes жизненно необходима, так как позволяет тонко настраивать систему или расширять ее функционал прямо на работающем производстве.
8. Возможность локального ввода/вывода. Как видно из рис. 4 контроллер Foxboro FCP270 рассчитан на работу только с удаленной подсистемой ввода/вывода, подключаемой к нему по оптическим каналам. Simatic S7-400 может спокойно работать как с локальными модулями ввода/вывода (свободные слоты на базовой панели есть), так и удаленными узлами.
9. Вес, габаритные размеры, вид монтажа (на DIN-рейку, на монтажную панель или в стойку 19”). Важно учитывать при проектировании и сборке системных шкафов.
10. Условия эксплуатации (температура, влажность, механические нагрузки). Большинство промышленных контроллеров могут работать в нечеловеческих условиях от 0 до 65 °С и при влажности до 95-98%.
[ http://kazanets.narod.ru/PLC_PART1.htm]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
DE
- speicherprogrammierbare Steuerung, f
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > программируемый логический контроллер
3 контроллер компенсации реактивной мощности
контроллер компенсации реактивной мощности
-
[Интент]EN
automatic reactive power regulator, controller
circuit designed to calculate the reactive power absorbed by the load connected to the power line and to control the switching on and off of the steps of the automatic bank, in order to compensate for the reactive power
NOTE 1 The reactive power is normally calculated at the fundamental frequency.
NOTE 2 The controller may be “built-in” or “free-standing” and has usually to be adjusted for each bank before operation.
[IEC 61921, ed. 1.0 (2003-04)]FR
régulateur varmétrique, régulateur
circuit conçu pour calculer la puissance réactive absorbée par la charge raccordée à l’alimentation de puissance et pour commander la connexion et la déconnexion des gradins de la batterie automatique de façon à compenser la puissance réactive
NOTE 1 La puissance réactive est normalement calculée à la fréquence fondamentale.
NOTE 2 Le régulateur peut être incorporé ou séparé et est normalement paramétré en fonction de la batterie avant fonctionnement.
[IEC 61921, ed. 1.0 (2003-04)]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
- automatic reactive power controller
- automatic reactive power regulator
- power factor controller
- reactive power controller
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > контроллер компенсации реактивной мощности
4 машина для контроля качества продукции
70. Машина для контроля качества продукции
D. Kontrollgerät für Packgut
E. Product quality controller
F. Machine de control du produit
Источник: ГОСТ 16299-78: Упаковывание. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > машина для контроля качества продукции
5 орган управления
орган управления
Частьсистемыаппарата управления, к которой прилагается извне усилие управления.
МЭК 60050(441-15-22).
Примечание. Орган управления может иметь форму рукоятки, ручки, нажимной кнопки, ролика, плунжера и т. п.
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60947-1-99)]
орган управления
Часть приводного механизма, к которой прикладывается внешняя сила воздействия.
Примечание - Орган управления может иметь форму ручки, кнопки, ролика, поршня и т.д.
[ ГОСТ Р 52726-2007]
орган управления
Часть системы привода, подвергаемая внешнему силовому воздействию.
Примечания
1. Орган управления может иметь форму ручки, рукоятки, нажимной кнопки, ролика, плунжера и т.д.
2. Есть несколько способов приведения в действие, которые не требуют внешнего силового воздействия, а только какого-либо действия.
[ГОСТ ЕН 1070-2003]
орган управления
Часть системы управления, которая предназначена непосредственно для воздействия оператором, например путем нажатия.
[ГОСТ Р ЕН 614-1-2003]
орган управления
Часть системы приведения в действие, которая принимает воздействие человека.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60447-2000]
орган управления
Часть системы приведения в действие, которая воспринимает воздействие человека (ГОСТ Р МЭК 60447).
Примечание
В настоящем стандарте орган управления в виде интерактивного экранного устройства отображения является частью этого устройства, которое представляет функцию органа управления.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60073-2000]
орган управления
Часть механизма прибора управления, на который оказывается вручную внешнее силовое воздействие.
Примечание.
Орган управления может иметь форму ручки, рукоятки, кнопки, ролика, плунжера и т.д.
Некоторые органы управления не требуют воздействия внешней силы, а только какого-либо действия.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60204-1-2007]
органы управления
Ручки, переключатели, потенциометры и другие органы, служащие для включения и регулировки аппаратуры. Термин относится преимущественно к аналоговым приборам.
[Система неразрушающего контроля. Виды (методы) и технология неразрушающего контроля. Термины и определения (справочное пособие). Москва 2003 г.]
орган управления
-
[IEV number 442-04-14]
средства оперирования
-
[Интент]EN
actuator
the part of the actuating system to which an external actuating force is applied
NOTE – The actuator may take the form of a handle, knob, push-button, roller, plunger, etc.
[IEV number 441-15-22]
actuator
part of a device to which an external manual action is to be applied
NOTE 1 The actuator may take the form of a handle, knob, push-button, roller, plunger, etc.
NOTE 2 There are some actuating means that do not require an external actuating force, but only an action.
NOTE 3 See also 3.34.
[IEC 60204-1 -2005]
actuating member
a part which is pulled, pushed, turned or otherwise moved to cause an operation of the switch
[IEV number 442-04-14]FR
organe de commande
partie du mécanisme transmetteur à laquelle un effort extérieur de manoeuvre est appliqué
NOTE – L'organe de commande peut prendre la forme d'une poignée, d'un bouton, d'un bouton-poussoir, d'une roulette, d'un plongeur, etc.
[IEV number 441-15-22]
organe de manoeuvre
partie qui est tirée, poussée, tournée ou manipulée de toute autre façon pour provoquer le fonctionnement de l'interrupteur
[IEV number 442-04-14]
Аппарат должен оставаться механически действующим. Не допускается сваривание контактов, препятствующее операции размыкания при использовании нормальных средств оперирования.
[ГОСТ Р 50030.3-99 (МЭК 60947-3-99) ]
ВДТ следует оперировать как при нормальной эксплуатации. Операции размыкания должны проводиться в следующем порядке:
для первых 1000 циклов — с использованием ручных средств оперирования;...
[ ГОСТ Р 51326. 1-99 ( МЭК 61008-1-96)]Параллельные тексты EN-RU
The operating means (for example, a handle) of the supply disconnecting device shall be easily accessible and located between 0,6 m and 1,9 m above the servicing level.
[IEC 60204-1-2006]Органы управления, например, рукоятки аппаратов отключения питания, должны быть легко доступны и располагаться на высоте от 0,6 до 1,9 м от рабочей площадки.
[Перевод Интент]Where the external operating means is not intended for emergency operations, it is recommended that it be coloured BLACK or GREY.
[IEC 60204-1-2006]Если внешние средства оперирования не предназначены для выполнения действий при возникновении аварийных ситуаций, то рекомендуется, применять такие средства ЧЕРНОГО или СЕРОГО цвета.
[Перевод Интент]1.2.2. Control devices
Control devices must be:
— clearly visible and identifiable and appropriately marked where necessary,
— positioned for safe operation without hesitation or loss of time, and without ambiguity,
— designed so that the movement of the control is consistent with its effect,
— located outside the danger zones, except for certain controls where necessary, such as emergency stop, console for training of robots,
— positioned so that their operation cannot cause additional risk,
— designed or protected so that the desired effect, where a risk is involved, cannot occur without an intentional operation,
— made so as to withstand foreseeable strain; particular attention must be paid to emergency stop devices liable to be subjected to considerable strain.1.2.2. Органы управления
Органы управления должны быть:
- четко видны, хорошо различимы и, где это необходимо, иметь соответствующее обозначение;
- расположены так, чтобы ими можно было пользоваться без возникновения сомнений и потерь времени на выяснение их назначения;
- сконструированы так, чтобы перемещение органа управления согласовывалось с их воздействием;
- расположены вне опасных зон; исключение, где это необходимо, делается для определенных средств управления, таких, как средство экстренной остановки, пульт управления роботом;
- расположены так, чтобы их использование не вызывало дополнительных рисков;
- сконструированы или защищены так, чтобы в случаях, где возможно возникновение рисков, они не могли бы возникнуть без выполнения намеренных действий;
- сделаны так, чтобы выдерживать предполагаемую нагрузку; при этом особое внимание уделяется органам аварийного останова, которые могут подвергаться значительным нагрузкам.Where a control is designed and constructed to perform several different actions, namely where there is no one-to-one correspondence (e.g. keyboards, etc.), the action to be performed must be clearly displayed and subject to confirmation where necessary.
Если орган управления предназначен для выполнения разных действий, например, если в качестве органа управления используется клавиатура или аналогичное устройство, то должна выводиться четкая информация о предстоящем действии, и, если необходимо, должно выполняться подтверждение на выполнение такого действия.
Controls must be so arranged that their layout, travel and resistance to operation are compatible with the action to be performed, taking account of ergonomic principles.
Органы управления должны быть организованы таким образом, чтобы их расположение, перемещение их элементов и усилие, которое оператор затрачивает на их перемещение, соответствовали выполняемым операциям и принципам эргономики.
Constraints due to the necessary or foreseeable use of personal protection equipment (such as footwear, gloves, etc.) must be taken into account.
Необходимо учитывать скованность движений операторов при использовании необходимых или предусмотренных средств индивидуальной защиты (таких, как специальная обувь, перчатки и др.).
Machinery must be fitted with indicators (dials, signals, etc.) as required for safe operation. The operator must be able to read them from the control position.
Для обеспечения безопасной эксплуатации машинное оборудование должно быть оснащено индикаторами (циферблатами, устройствами сигнализации и т. д.). Оператор должен иметь возможность считывать их с места управления.
From the main control position the operator must be able to ensure that there are no exposed persons in the danger zones.
Находясь в главном пункте управления, оператор должен иметь возможность контролировать отсутствие незащищенных лиц.
If this is impossible, the control system must be designed and constructed so that an acoustic and/ or visual warning signal is given whenever the machinery is about to start.
Если это невозможно, то система управления должна быть разработана и изготовлена так, чтобы перед каждым пуском машинного оборудования подавался звуковой и/или световой предупредительный сигнал.
The exposed person must have the time and the means to take rapid action to prevent the machinery starting up.
[DIRECTIVE 98/37/EC OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL]
Незащищенное лицо должно иметь достаточно времени и средств для быстрого предотвращения пуска машинного оборудования.
[Перевод Интент]
Тематики
- автоматизация, основные понятия
- аппарат, изделие, устройство...
- безопасность машин и труда в целом
- выключатель автоматический
- выключатель, переключатель
- высоковольтный аппарат, оборудование...
- электробезопасность
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
- actuating member
- actuator
- command unit
- control
- control device
- controller
- controls
- operating control
- operating means
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > орган управления
6 quality
(a) (standard) qualité f;∎ of good/poor quality de bonne/mauvaise qualité;∎ we have a reputation for quality nous sommes réputés pour la qualité de nos produitsquality assurance garantie f de qualité;quality audit audit m de qualité;quality circle cercle m de qualité;quality control contrôle m de la qualité;quality control department service m contrôle de la qualité;quality controller responsable m f du contrôle de la qualité;quality goods marchandises f pl de qualité;quality improvement amélioration f de la qualité;quality label label m de qualité;quality management gestion f qualité;MARKETING quality positioning positionnement m par la qualité(b) (attribute) qualité f;∎ these are the qualities we are looking for in our candidates voici les qualités que nous recherchons chez nos candidats7 traffic
1 noun∎ holiday traffic (outward) la circulation des grands départs; (homeward) la circulation des grands retours;∎ the traffic is heavy/light la circulation est dense/fluide;∎ traffic is building up la circulation augmente;∎ there is a great deal of traffic on the roads les routes sont encombrées;∎ traffic in and out of the city circulation à destination et en provenance de la ville;∎ watch out for traffic when crossing! (fais) attention aux voitures en traversant!;∎ road closed to heavy traffic route interdite aux poids lourds;∎ eastbound traffic circulation f ouest-est;∎ the cyclist weaved through the traffic le cycliste se faufila entre les voitures;∎ figurative the resort experiences heavy ski traffic in winter il y a beaucoup de skieurs en hiver dans cette station∎ the traffic in arms/drugs le trafic des armes/de drogue∎ you should have no traffic with these people évitez d'avoir affaire à ces gens∎ to traffic in faire le commerce de;∎ organizations trafficking in arms/drugs des organisations spécialisées dans le trafic d'armes/de drogue;∎ figurative reporters who traffic in human misery journalistes qui exploitent la misère humainetraffic calming contrôle m de la circulation;American traffic circle rond-point m, sens m giratoire;traffic cone cône m de signalisation (pour la circulation routière);Aviation traffic controller contrôleur(euse) m,f de la navigation aérienne, aiguilleur m du ciel;Aviation traffic control tower tour f de contrôle;American traffic court = tribunal chargé des infractions au code de la route;traffic island refuge m;British traffic jam embouteillage m, bouchon m;traffic lights feu m de signalisation;∎ the traffic lights are (at) green le feu est (au) vert;∎ carry on to the next set of traffic lights continuez jusqu'aux prochains feux;traffic offence infraction f au code de la route;traffic patrol patrouille f de la circulation (routière);Aviation traffic pattern couloir m ou position f d'approche;traffic police (for speeding, safety) police f de la route; (on point duty) agents mpl de la circulation;traffic policeman agent m de police; (on point duty) agent m de la circulation;traffic sign panneau m de signalisation, poteau m indicateur;traffic signal feu m de signalisation;American traffic violation infraction f au code de la route;British traffic warden contractuel(elle) m,fⓘ TRAFFIC WARDEN En Grande-Bretagne, les contractuels sont habilités à dresser les procès-verbaux mais aussi à régler la circulation.8 air
air [εər]1. nouna. air m• there's a rumour in the air that... le bruit court que...► off airb. ( = manner) air ma. [+ clothes, bed] aérerb. [+ opinions] faire connaître ; [+ idea, proposal] émettre( = be broadcast) être diffusé4. compounds► air show noun ( = trade exhibition) salon m de l'aéronautique ; ( = flying display) meeting m aérien* * *[eə(r)] 1.1) ( substance) air min the open air — en plein air, au grand air
to come up for air — [swimmer, animal] remonter à la surface pour respirer
2) (atmosphere, sky) air mby air — Postal services par avion
to clear the air — lit [storm] rafraîchir l'air; fig apaiser les esprits
3) Radio, Televisionto be/go on the air — [broadcaster, interviewee] être/passer à l'antenne
off the air, she confided that... — hors antenne, elle a confié que...
to go off the air — [channel] cesser d'émettre
5) Music air m2. 3.transitive verb2) ( express) exprimer [opinion, view]••there's a rumour in the air that... — le bruit court que...
to put on airs —
to give oneself airs — péj se donner de grands airs
to be up in the air — fig [plans] être très flou
9 quality
10 credit
1 noun(a) (for future payment) crédit m;∎ to give sb credit faire crédit à qn;∎ to buy/sell sth on credit acheter/vendre qch à crédit;∎ her credit is good elle a une bonne réputation de solvabilitécredit account BANKING compte m créditeur; (with shop) compte client; credit advice avis m de crédit;credit agency agence f de crédit;credit agreement accord m ou convention f de crédit;credit application form formule f de demande de crédit;credit bank banque f de crédit;credit broker courtier(ère) m, f en crédits ou en prêts;American credit bureau agence de notation;credit call = appel téléphonique effectué avec une carte de crédit;credit card carte f de crédit;credit card fraud usage m frauduleux de cartes de crédit;credit card number numéro m de carte de crédit;credit card transaction transaction f effectuée par carte de crédit;credit ceiling plafond m de crédit;credit control encadrement m du crédit;credit controller contrôleur(euse) m, f du crédit;credit crunch resserrement m du crédit;credit enquiry renseignements m pl de crédit, enquête f de solvabilité;credit facilities facilités f pl de crédit;∎ to give sb credit facilities accréditer qn (auprès d'une banque);credit file dossier m crédit;credit freeze blocage m du crédit, gel m des crédits;credit guarantee fund caisse f de garantie;credit history profil m crédit;∎ to obtain information on sb's credit history établir des renseignements de solvabilité sur qn;credit institution établissement m de crédit;credit insurance assurance-crédit f;credit limit limite f de crédit, plafond de crédit;credit management direction f des crédits;credit manager directeur(trice) m, f des crédits;credit margin marge f de crédit;credit options formules f pl de crédit;credit organization organisme m de crédit;credit period délai m de crédit;credit purchase achat m à crédit;credit rating (of person, company) degré m de solvabilité; FINANCE (awarded by credit reference agency) notation f;credit rating agency agence de notation;credit restrictions encadrement du crédit;credit risk risque m de crédit;credit sale vente f à crédit;credit scoring méthode f d'évaluation de la solvabilité, crédit-scoring m;credit squeeze encadrement du crédit;credit terms modalités f pl du crédit;credit transaction transaction à crédit;American credit union société f ou caisse f de créditcredit entry ACCOUNTANCY écriture f passée au crédit; BANKING article m porté au crédit d'un compte;ACCOUNTANCY credit item poste m créditeur;credit memo bulletin m de versement;BANKING credit transfer virement m;credit voucher chèque m de caisse(account) créditer;∎ to credit an account with £200, to credit £200 to an account créditer un compte de 200 livresThe Money Store, which has 140 employees at branches in Glasgow, Birmingham, Bristol, Manchester, Newcastle and Warrington, is focused on customers such as the self-employed and divorced who can suffer difficulties in getting a credit rating from high street lenders.
11 financial
financier(ère)financial accountant comptable m f financier(ère);financial accounting comptabilité f financière;financial administration gestion f financière;financial adviser conseiller(ère) m, f financier(ère);financial aid aide f financière;financial analyst analyste m f financier(ère);financial appraisal évaluation f financière;financial arrangement montage m financier;financial assistance appui m financier;financial authorities autorités f pl financières;financial backer bailleur(eresse) m, f de fonds;financial backing financement m, aide f financière;financial centre place f financière;financial chart graphique m financier;financial circles milieux m pl financiers;financial community communauté f financière;financial compensation contrepartie f financière;financial consultant conseiller(ère) financier(ère);financial control contrôle m financier;financial controller contrôleur(euse) m, f financier(ère);ACCOUNTANCY financial costs frais m pl financiers;financial crisis crise f financière;ACCOUNTANCY financial deal opération f financière;financial difficulties difficultés f pl financières, difficultés de trésorerie;financial director directeur(trice) m, f financier(ère);financial engineering ingénierie f financière;financial expenses charges f pl financières;STOCK EXCHANGE financial future instrument m financier à terme;STOCK EXCHANGE financial futures market marché m d'instruments financiers à terme;financial gearing effet m de levier financier;financial group groupe m financier;financial healthcheck diagnostic m financier;financial imbalance déséquilibre m financier;financial institution établissement m financier;financial instrument instrument financier;financial intermediary intermédiaire m f financier(ère);financial journal revue f financière;financial management direction f ou gestion f financière;financial manager directeur(trice) financier(ère);financial market marché financier;financial means moyens m pl financiers;financial news chronique f financière;financial ombudsman arbitre m financier;financial partner partenaire m f financier(ère);financial period période f comptable;financial plan plan m de financement;financial planning planification f financière;financial pool groupement m financier;financial position position f ou situation f financière;financial press presse f financière;financial pressure problèmes m pl financiers;financial product produit m financier;ACCOUNTANCY financial ratio ratio m de gestion;ACCOUNTANCY financial report rapport m financier;ACCOUNTANCY financial reporting communication f de l'information financière;British Financial Reporting Council = commission de contrôle de la qualité de l'information financière publiée par les entreprises;financial resources ressources f pl financières;financial review examen m financier;financial services services m pl financiers;Financial Services Authority = organisme gouvernemental britannique chargé de contrôler les activités du secteur financier;financial situation situation financière;financial statement état m financier, déclaration f de résultats;financial strategy stratégie f financière;financial support soutien m financier;financial syndicate syndicat m financier;Financial Times All-Share Index = indice boursier du Financial Times basé sur la valeur de 700 actions cotées à la Bourse de Londres;Financial Times-(Industrial) Ordinary Share Index = indice boursier du Financial Times basé sur la valeur de 30 actions cotées à la Bourse de Londres;Financial Times-Stock Exchange 100 Share Index = principal indice boursier du Financial Times basé sur la valeur de 100 actions cotées à la Bourse de Londres;financial transaction opération financière;British financial year exercice m (comptable)12 air-traffic
►► Aviation air-traffic control contrôle m du trafic aérien;Aviation air-traffic controller contrôleur(euse) m,f du trafic aérien, aiguilleur m du cielUn panorama unique de l'anglais et du français > air-traffic
13 credit
credit ['kredɪt]crédit ⇒ 1 (a) mérite ⇒ 1 (b) croyance ⇒ 1 (c) unité de valeur ⇒ 1 (d) créditer ⇒ 3 (a) supposer ⇒ 3 (b) croire ⇒ 3 (c) générique ⇒ 41 noun∎ he has £50 to his credit il a 50 livres sur son compte, il a un avoir de 50 livres;∎ to enter or to place a sum to sb's credit créditer le compte de qn d'une somme, porter une somme à l'actif de qn;∎ debit and credit débit m et crédit m;∎ to give sb credit, to give credit to sb (of bank) accorder un découvert à qn; (of shop, pub) faire crédit à qn;∎ to run a credit check on sb (to ensure enough money in account) vérifier la solvabilité de qn, vérifier que le compte de qn est approvisionné; (to ensure no record of bad debts) vérifier le passé bancaire de qn;∎ we do not give credit (sign) la maison ne fait pas crédit;∎ to sell/to buy/to live on credit vendre/acheter/vivre à crédit;∎ her credit is good elle a une bonne réputation de solvabilité; figurative (she is trustworthy) elle est digne de confiance;∎ figurative isn't my credit good any more? on ne me fait plus confiance?(b) (merit, honour) mérite m;∎ all the credit should go to the team tout le mérite doit revenir à l'équipe;∎ to take the credit for sth/doing sth s'attribuer le mérite de qch/d'avoir fait qch;∎ I can't take all the credit for it tout le mérite ne me revient pas;∎ to give sb the credit for sth/doing sth attribuer à qn le mérite de qch/d'avoir fait qch;∎ management got all the credit tout le mérite est revenu à la direction;∎ give her credit for what she has achieved reconnais ce qu'elle a accompli;∎ with credit (perform) honorablement;∎ nobody emerged with any credit except him c'est le seul qui s'en soit sorti à son honneur;∎ it must be said to his credit that… il faut dire en sa faveur que…;∎ to her credit she did finish the exam il faut lui accorder qu'elle a fini l'examen;∎ she has five novels to her credit elle a cinq romans à son actif;∎ to be a credit to one's family/school, to do one's family/school credit faire honneur à sa famille/son école, être l'honneur de sa famille/son école;∎ it does her (great) credit c'est tout à son honneur;∎ it does you credit that you gave the money back c'est tout à votre honneur d'avoir rendu l'argent;∎ give me SOME credit! je ne suis quand même pas si bête!;∎ credit where credit is due il faut reconnaître ce qui est(c) (credence) croyance f;∎ to give credit to sb/sth ajouter foi à qn/qch;∎ to lend credit to sth accréditer qch, rendre qch plausible;∎ the theory is gaining credit cette théorie est de plus en plus acceptée;∎ he's cleverer than I gave him credit for il est plus intelligent que je le pensais ou supposais;∎ I gave you credit for more sense je vous supposais plus de bon sens;∎ I gave him credit for more sense than I perhaps should have done j'ai peut-être surestimé son bon sens(d) University unité f de valeur, UV f;∎ how many credits do you need? combien d'UV faut-il que tu aies?∎ to credit an account with £200, to credit £200 to an account créditer un compte de 200 livres∎ to credit sb with intelligence/tact/sense supposer de l'intelligence/du tact/du bon sens à qn;∎ I credited her with more sense je lui supposais plus de bon sens;∎ credit me with a bit more intelligence! tu serais gentil de ne pas sous-estimer mon intelligence!;∎ she is credited with being the first woman to attend medical school elle est considérée comme la première femme à avoir fait des études de médecine;∎ he is credited with the discovery of DNA on lui attribue la découverte de l'ADN∎ would you credit it! tu te rends compte!;∎ you wouldn't credit some of the things he's done tu n'en reviendrais pas si tu savais les choses qu'il a faites;∎ I could hardly credit it j'avais du mal à le croireCinema & Television générique mcredit advice avis m de crédit;credit agency institution f de crédit;credit agreement accord m ou convention f de crédit;credit bank banque f de crédit;credit broker courtier(ère) m,f en crédits ou en prêts;American credit bureau institution f de crédit;credit card carte f de crédit;∎ to pay by credit card payer avec une ou régler par carte de crédit;credit card fraud usage m frauduleux de cartes de crédit;credit card number numéro m de carte de crédit;credit card reader lecteur m de cartes;credit card transactions transactions fpl effectuées par carte de crédit;credit ceiling plafond m de crédit;Accountancy credit column colonne f créditrice;credit control (government restrictions) resserrement m ou encadrement m du crédit; (monitoring) surveillance m des crédits;credit controller contrôleur(euse) m,f du crédit;credit enquiry renseignements mpl de crédit, enquête f de solvabilité;credit entry Banking article m porté au crédit d'un compte; Accountancy écriture f au crédit;credit facilities facilités fpl de crédit;credit freeze blocage m du crédit;credit history profil m crédit;∎ to obtain information on sb's credit history établir des renseignements de solvabilité sur qn;credit institution établissement m de crédit;credit insurance assurance-crédit f;Accountancy credit item poste m créditeur;credit limit limite f ou plafond m de crédit;credit line British (loan) autorisation f de crédit; American (limit) limite f ou plafond m de crédit;credit management direction f des crédits;credit manager directeur(trice) m,f du crédit;credit margin marge f de crédit;credit memo bulletin m de versement;credit period délai m de crédit;credit rating (of person, company) degré m de solvabilité; (awarded by credit reference agency) notation f;credit rating agency agence f de notation;credit risk risque m de crédit;∎ to be a good/bad credit risk représenter un risque peu important/important;credit scoring = méthode d'évaluation de la solvabilité, crédit-scoring m;Accountancy credit side crédit m, avoir m;∎ figurative on the credit side, the proposed changes will cut costs les changements projetés auront l'avantage de réduire les coûts;∎ figurative on the credit side, he's a good cook il faut lui accorder qu'il cuisine bien;credit squeeze restriction f ou encadrement m du crédit;∎ there's a credit squeeze le crédit est restreint ou encadré;credit terms modalités fpl de crédit;Banking credit transfer virement m, transfert m (de compte à compte);American credit union société f ou caisse f de crédit;credit voucher chèque m de caisse14 financial
financial [faɪ'nænʃəl]financier;∎ but does it make financial sense? mais est-ce que c'est avantageux ou intéressant du point de vue financier?►► financial accountant comptable mf financier(ère);financial accounting comptabilité f générale ou financière;financial administration gestion f financière;financial adviser conseiller(ère) m,f financier(ère);financial aid aide f financière;financial analyst analyste mf financier(ère);financial appraisal évaluation f financière;financial assistance appui m financier, aide f financière;financial backer bailleur(eresse) m,f de fonds;financial backing financement m, aide f financière;financial centre place f financière;financial consultant conseiller(ère) m,f financier(ère), conseil m financier;financial control contrôle m financier;financial controller contrôleur(euse) m,f financier(ère);Accountancy financial costs frais mpl financiers;financial deal opération f financière;financial director directeur(trice) m,f financier(ère);financial engineering ingénierie f financière;financial expenses charges fpl financières;Stock Exchange financial future instrument m financier à terme;Stock Exchange financial futures exchange bourse f d'instruments financiers à terme;financial gearing effet m de levier financier;financial healthcheck diagnostic m financier;financial institution établissement m financier;financial instrument instrument m financier;financial intermediary intermédiaire mf financier(ère);financial management direction f ou gestion f financière;financial manager directeur(trice) m,f financier(ère);financial market marché m financier;Radio & Television financial news chronique f financière;financial ombudsman arbitre m financier;financial pages pages fpl financières;financial partner partenaire mf financier(ère);financial period période f comptable;financial plan plan m de financement;financial planning planification f financière;financial position position f ou situation f financière;financial pressure problèmes mpl financiers;financial product produit m financier;financial ratio ratio m de gestion;financial report rapport m financier;financial reporting communication f de l'information financière;British Financial Reporting Council = commission de contrôle de la qualité de l'information financière publiée par les entreprises;financial resources ressources fpl;financial services services mpl financiers;Financial Services Authority = organisme gouvernemental britannique chargé de contrôler les activités du secteur financier;financial situation situation f financière;financial statement état m financier, déclaration f de résultats;financial syndicate syndicat m financier;Press The Financial Times = quotidien britannique d'information financière;Finance Financial Times All-Share Index = indice boursier du Financial Times basé sur la valeur de 700 actions cotées à la Bourse de Londres;Finance Financial Times-(Industrial) Ordinary Share Index = indice boursier du Financial Times basé sur la valeur de 30 actions cotées à la Bourse de Londres;Finance Financial Times-Stock Exchange 100 Share Index = principal indice boursier du Financial Times basé sur la valeur de 100 actions cotées à la Bourse de Londres;financial transaction opération f financière;ⓘ FINANCIAL TIMES Le Financial Times est un quotidien britannique de qualité, spécialisé dans l'actualité financière et économique; il est reconnaissable à la couleur rose de son papier. Il existe une édition internationale, diffusée notamment en Allemagne et en France.ⓘ FINANCIAL YEAR Pour les impôts sur le revenu en Grande-Bretagne, l'année fiscale commence le 5 avril.15 mission
mission ['mɪʃən]∎ mission of inquiry mission f d'enquête;∎ he was sent on a rescue mission il fut envoyé en mission de sauvetage;∎ she's found her mission in life elle a trouvé sa vraie vocation;∎ his mission in life is to raise awareness of the environment il tient absolument à sensibiliser l'opinion publique aux problèmes d'environnement∎ a Chinese trade mission une mission commerciale chinoise(c) (organization, charity) mission f;∎ Mission to Seamen Mission f aux Marins∎ he had flown twenty missions il avait effectué vingt missions;∎ mission accomplished mission accomplie►► mission control centre m de contrôle;mission controller chef m du centre de contrôle;mission creep = opération militaire dont les objectifs ne sont pas clairement définis et qui risque de s'éterniser;mission statement ordre m de mission;mission station mission f16 quality
1 noun(a) (standard, nature) qualité f;∎ the high/poor quality of the workmanship la bonne/mauvaise qualité du travail;∎ the quality of life la qualité de la vie(b) (high standard, excellence) qualité f;∎ quality matters more than quantity la qualité importe plus que la quantité;∎ never mind the price, I'm only interested in quality peu importe le prix, ce que je recherche, c'est la qualité;∎ we have a reputation for quality nous sommes réputés pour la qualité de nos produits(c) (feature, attribute) qualité f;∎ these are the qualities we are looking for in our candidates voici les qualités que nous recherchons chez nos candidats;∎ he has a lot of good qualities il a de nombreuses qualités;∎ I don't doubt her intellectual qualities je ne doute pas de ses capacités intellectuelles;∎ these tyres have superior road-holding qualities ces pneus offrent une meilleure adhérence au sol(d) British (newspaper) = quotidien ou journal du dimanche de qualité (par opposition à la presse populaire)∎ a gentleman of quality un homme de qualité;∎ the quality les gens mpl de qualité, pejorative le beau linge(goods, work, shop) de qualité;∎ I only spend an hour in the evening with my kids, but it's quality time je ne passe qu'une heure avec mes gosses le soir, mais je profite bien d'eux►► quality assurance garantie f de qualité;quality audit audit m de qualité;British quality circle cercle m de qualité;quality control contrôle m de (la) qualité;quality controller responsable mf du contrôle de (la) qualité, qualiticien(enne) m,f;quality improvement l'amélioration f de la qualité;quality label label m de qualité;quality management gestion f qualité;British quality newspaper = quotidien ou journal du dimanche de qualité (par opposition à la presse populaire);Marketing quality positioning positionnement m par la qualitéСм. также в других словарях:
Controller (Marvel Comics) — Controller Controller Publication information Publisher Marvel Comics … Wikipedia
Controller area network — Controller–area network (CAN or CAN bus) is a vehicle bus standard designed to allow microcontrollers and devices to communicate with each other within a vehicle without a host computer. CAN is a message based protocol, designed specifically for… … Wikipedia
Control engineering — Control systems play a critical role in space flight Control engineering or Control systems engineering is the engineering discipline that applies control theory to design systems with predictable behaviors. The practice uses sensors to measure… … Wikipedia
Controller-area network — (CAN or CAN bus) is a computer network protocol and bus standard designed to allow microcontrollers and devices to communicate with each other without a host computer.It was designed specifically for automotive applications but is now also used… … Wikipedia
Control reconfiguration — is an active approach in control theory to achieve fault tolerant control for dynamic systems [1]. It is used when severe faults, such as actuator or sensor outages, cause a break up of the control loop, which must be restructured to prevent… … Wikipedia
Controller General of Defence Accounts — (CGDA) is one of the oldest government organisations in India. CGDA operates under the Defence Accounts Department (DAD) of the Ministry of Defence of India. Its origins goes back to the Article of War adopted by the British Parliament in April… … Wikipedia
Controller Pilot Data Link Communications — (CPDLC), also referred to as Controller Pilot Data Link (CPDL), is a method by which air traffic controllers can communicate with pilots over a datalink system. Contents 1 Necessity 2 Use of CPDLC 3 Implementation … Wikipedia
Controller — may refer to: Contents 1 Occupations 2 Computing and electronics 3 Other devices … Wikipedia
Controller — Con*trol ler, n. [From control, v. t.: cf. F. contr[^o]leur.] 1. One who, or that which, controls or restraines; one who has power or authority to regulate or control; one who governs. [1913 Webster] The great controller of our fate Deigned to be … The Collaborative International Dictionary of English
controller — Con*trol ler, n. [From control, v. t.: cf. F. contr[^o]leur.] 1. One who, or that which, controls or restraines; one who has power or authority to regulate or control; one who governs. [1913 Webster] The great controller of our fate Deigned to be … The Collaborative International Dictionary of English
controller — control ► NOUN 1) the power to influence people s behaviour or the course of events. 2) the restriction of an activity or phenomenon. 3) a means of limiting or regulating something: exchange controls. 4) a device by which a machine is regulated.… … English terms dictionary
Перевод: со всех языков на французский
с французского на все языки- С французского на:
- Все языки
- Со всех языков на:
- Все языки
- Албанский
- Английский
- Арабский
- Венгерский
- Вьетнамский
- Греческий
- Датский
- Исландский
- Испанский
- Итальянский
- Казахский
- Каталанский
- Латышский
- Литовский
- Монгольский
- Немецкий
- Норвежский
- Персидский
- Польский
- Португальский
- Румынский, Молдавский
- Русский
- Словацкий
- Словенский
- Турецкий
- Украинский
- Финский
- Французский
- Чешский
- Шведский
